|
|
@@ -14,8 +14,27 @@
|
|
|
</div>
|
|
|
<div class="span9">
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Introduction and Overview
|
|
|
-=========================
|
|
|
+# Editor / Notebook
|
|
|
+## SQL
|
|
|
+## Jobs
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+# Dashboard
|
|
|
+## SQL
|
|
|
+## Elastic Search
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+# Browsers
|
|
|
+## Jobs
|
|
|
+e.g. Spark Livy, Impala Query Browser
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+## Files
|
|
|
+e.g. ADLS
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+# Metadata
|
|
|
+## Data Catalog
|
|
|
+## Optimization
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+# New application
|
|
|
+## Introduction and Overview
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hue leverages the browser to provide users with an environment for exploring
|
|
|
and analyzing data.
|
|
|
@@ -35,8 +54,7 @@ This document will orient you with the general structure of Hue
|
|
|
and will walk you through adding a new application using the SDK.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-From 30,000 feet
|
|
|
-----------------
|
|
|
+### From 30,000 feet
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -44,8 +62,7 @@ Hue, as a "container" web application, sits in between your Hadoop installation
|
|
|
and the browser. It hosts all the Hue Apps, including the built-in ones, and
|
|
|
ones that you may write yourself.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-The Hue Server
|
|
|
---------------
|
|
|
+### The Hue Server
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -67,8 +84,7 @@ typically communicate with these side daemons
|
|
|
by using Thrift (e.g., for Hive query execution) or by exchanging state
|
|
|
through the database.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Interacting with Hadoop
|
|
|
------------------------
|
|
|
+### Interacting with Hadoop
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -78,16 +94,14 @@ interacting with HDFS. These APIs work by making REST API or Thrift calls
|
|
|
the Hadoop daemons. The Hadoop administrator must enable these interfaces from
|
|
|
Hadoop.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-On the Front-End
|
|
|
-----------------
|
|
|
+### On the Front-End
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hue provides a front-end framework based on
|
|
|
[Bootstrap](http://twitter.github.com/bootstrap/) and
|
|
|
[Knockout js](http://knockoutjs.com/).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-An Architectural View
|
|
|
----------------------
|
|
|
+### An Architectural View
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -107,8 +121,8 @@ Many apps will evolve to have a bit of custom JavaScript and
|
|
|
CSS styles. Apps that need to talk to an external service
|
|
|
will pull in the code necessary to talk to that service.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-File Layout
|
|
|
------------
|
|
|
+### File Layout
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
The Hue "framework" is in ``desktop/core/`` and contains the Web components.
|
|
|
``desktop/libs/`` is the API for talking to various Hadoop services.
|
|
|
The installable apps live in ``apps/``. Please place third-party dependencies in the app's ext-py/
|
|
|
@@ -139,22 +153,20 @@ The typical directory structure for inside an application includes:
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the URLs within your application, you should make your own ``urls.py``
|
|
|
which will be automatically rooted at ``/yourappname/`` in the global
|
|
|
-namespace. See ``apps/about/src/about/urls.py`` for an example.
|
|
|
+namespace. See ``apps/about/src/about/urls.py`` for an example.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
|
+## Pre-requisites
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Pre-requisites
|
|
|
-==============
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Software
|
|
|
---------
|
|
|
+### Software
|
|
|
|
|
|
Developing for the Hue SDK has similar requirements to running
|
|
|
Hue itself. We require python (2.6 to 2.7), Django (1.6 included
|
|
|
with our distribution), Hadoop (Apache Hadoop 2+), Java (Sun Java 1.8),
|
|
|
and Browser (latest Chrome, Firefox or IE9+).
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Recommended Reading / Important Technologies
|
|
|
---------------------------------------------
|
|
|
+### Recommended Reading / Important Technologies
|
|
|
|
|
|
The following are core technologies used inside of Hue.
|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -165,14 +177,12 @@ The following are core technologies used inside of Hue.
|
|
|
between daemons.
|
|
|
* [Mako](http://www.makotemplates.org/) is the preferred templating language.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Fast-Guide to Creating a New Hue Application
|
|
|
-============================================
|
|
|
+## Fast-Guide to Creating a New Hue Application
|
|
|
|
|
|
Now that we have a high-level overview of what's going on,
|
|
|
let's go ahead and create a new installation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Download, Unpack, Build Distro
|
|
|
-------------------------------
|
|
|
+### Download, Unpack, Build Distro
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Hue SDK is available from [Github](http://github.com/cloudera/hue). Releases
|
|
|
can be found on the [download page](http://gethue.com/category/release/).
|
|
|
@@ -190,8 +200,7 @@ it is preferable to checkout a particular release tag instead.
|
|
|
## Visit http://localhost:8000/ with your web browser.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Run "create_desktop_app" to Set up a New Source Tree
|
|
|
---------------------------------------------
|
|
|
+### Run "create_desktop_app" to Set up a New Source Tree
|
|
|
|
|
|
./build/env/bin/hue create_desktop_app calculator
|
|
|
find calculator -type f
|
|
|
@@ -219,8 +228,7 @@ To download an app or browse dditional plugin apps available in the Hue app stor
|
|
|
Check the hue.ini 'app_blacklist' parameter for details.
|
|
|
</div>
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Install SDK Application
|
|
|
------------------------
|
|
|
+### Install SDK Application
|
|
|
|
|
|
As you'll discover if you look at calculator's <tt>setup.py</tt>,
|
|
|
Hue uses a distutils <tt>entrypoint</tt> to
|
|
|
@@ -263,14 +271,10 @@ You can now browse the new application.
|
|
|
build/env/bin/hue runserver
|
|
|
|
|
|
And then visit <a href="http://localhost:8000">http://localhost:8000/</a> to check it out!
|
|
|
-You should see the app (with a boring "SDK" icon) in the dock, and clicking it
|
|
|
-will bring up a boring screen:
|
|
|
+You should see the app in the left menu.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-<img src="new_app_in_dock.png">
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Customizing Views and Templates
|
|
|
--------------------------------
|
|
|
+### Customizing Views and Templates
|
|
|
|
|
|
Now that your app has been installed, you'll want to customize it.
|
|
|
As you may have guessed, we're going to build a small calculator
|
|
|
@@ -337,46 +341,20 @@ should see something like:
|
|
|
<img src="calculator_working.png">
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-A Look at some Existing Apps
|
|
|
-============================
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
+## A Look at some Existing Apps
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Help
|
|
|
-----
|
|
|
+### Job Browser
|
|
|
|
|
|
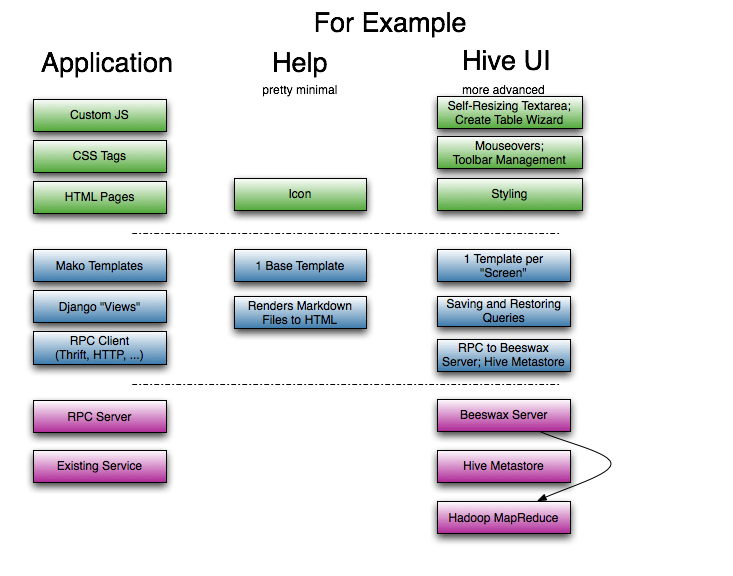
-The Help application is as minimal as they get. Take a look at it!
|
|
|
-The core logic is in the "views.py" file. The central function
|
|
|
-there takes `(app, path)` (which are mapped from the request URL
|
|
|
-by the regular expression in `urls.py`). The view function
|
|
|
-finds the data file that needs to be rendered, renders it through
|
|
|
-the markdown module, if necessary, and then displays it through
|
|
|
-a simple template.
|
|
|
+### ADLS Browser
|
|
|
|
|
|
-You'll note that the "Help Index" is presented in a "split view".
|
|
|
-No JavaScript was written to make this happen! Instead, the template
|
|
|
-applied certain CSS classes to the relevant `div`'s, and JFrame
|
|
|
-did the rest.
|
|
|
|
|
|
+## Backend Development
|
|
|
|
|
|
-SQL Hive Editor
|
|
|
----------------
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-The Hive Editor (old named Beeswax) is on the opposite end of the complexity scale from Help.
|
|
|
-In addition to many views (in `views.py`), Beeswax uses
|
|
|
-Django Forms for server-side form validation (the forms are in `forms.py`),
|
|
|
-several features of the Mako templating engine (especially includes and
|
|
|
-functions), a separate server (implemented in Java), and significant
|
|
|
-JavaScript for user interaction.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Backend Development
|
|
|
-===================
|
|
|
|
|
|
This section goes into greater detail on useful features within
|
|
|
the Hue environment.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-User Management
|
|
|
----------------
|
|
|
+### User Management
|
|
|
|
|
|
Except for static content, `request.user` is always populated. It is a
|
|
|
standard Django `models.User` object. If you were to set a breakpoint at the
|
|
|
@@ -394,10 +372,9 @@ standard Django `models.User` object. If you were to set a breakpoint at the
|
|
|
user is authenticated.
|
|
|
</div>
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Configuration
|
|
|
--------------
|
|
|
+### Configuration
|
|
|
|
|
|
-### Configuration File
|
|
|
+#### Configuration File
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hue uses a typed configuration system that reads configuration files (in an
|
|
|
ini-style format). By default, Hue loads all `*.ini` files in the `build/desktop/conf`
|
|
|
@@ -419,7 +396,7 @@ directory. The configuration files have the following format:
|
|
|
# namenode_host = 10.0.0.1
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-### Configuration Variables
|
|
|
+#### Configuration Variables
|
|
|
|
|
|
Your application's `conf.py` is special. It provides access to the configuration file (and even
|
|
|
default configurations not specified in the file). Using the above example, your `conf.py` should
|
|
|
@@ -488,8 +465,7 @@ function in your `conf.py`:
|
|
|
</div>
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Running "Helper Processes"
|
|
|
---------------------------
|
|
|
+#### Running "Helper Processes"
|
|
|
|
|
|
Some Hue applications need to run separate daemon processes on the side.
|
|
|
For example, `BeeswaxServer` is responsible for managing Hive query states.
|
|
|
@@ -527,8 +503,7 @@ the stored state in a database or run a separate server.
|
|
|
|
|
|
<!-- "Wheel reinvention" Supervisor is following the Erlang model. -->
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Walk-through of a Django View
|
|
|
------------------------------
|
|
|
+### Walk-through of a Django View
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -541,8 +516,7 @@ These view functions typically use their arguments (for example, the captured pa
|
|
|
their request object (which has, for example, the POST and GET parameters) to
|
|
|
prepare dynamic content to be rendered using a template.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Templates: Django and Mako
|
|
|
---------------------------
|
|
|
+#### Templates: Django and Mako
|
|
|
|
|
|
In Hue, the typical pattern for rendering data through a template
|
|
|
is:
|
|
|
@@ -557,8 +531,7 @@ extension of the template file (".html" or ".mako"). Mako templates are more pow
|
|
|
in that they allow you to run arbitrary code blocks quite easily, and are more strict (some
|
|
|
would say finicky); Django templates are simpler, but are less expressive.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Django Models
|
|
|
--------------
|
|
|
+### Django Models
|
|
|
|
|
|
[Django Models](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/#the-model-layer)
|
|
|
are Django's Object-Relational Mapping framework. If your application
|
|
|
@@ -568,8 +541,7 @@ From an abstraction perspective, it's common to imagine external services
|
|
|
as "models". For example, the Job Browser treats the Hadoop JobTracker
|
|
|
as a "model", even though there's no database involved.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Accessing Hadoop
|
|
|
-----------------
|
|
|
+### Accessing Hadoop
|
|
|
|
|
|
It is common for applications to need to access the underlying HDFS.
|
|
|
The `request.fs` object is a "file system" object that exposes
|
|
|
@@ -592,8 +564,7 @@ of functions available is as follows:
|
|
|
`stats`.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Making Your Views Thread-safe
|
|
|
------------------------------
|
|
|
+### Making Your Views Thread-safe
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hue works in any WSGI-compliant container web server.
|
|
|
The current recommended deployment server is the built-in CherryPy server.
|
|
|
@@ -617,8 +588,7 @@ there still may be multiple copies of this state.
|
|
|
For persistent global state, it is common to place the state
|
|
|
in the database or on the Browser local storage.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Authentication Backends
|
|
|
------------------------
|
|
|
+## Authentication Backends
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hue exposes a configuration flag ("auth") to configure
|
|
|
a custom authentication backend. See
|
|
|
@@ -629,8 +599,7 @@ In addition to that, backends may support a `manages_passwords_externally()` met
|
|
|
True or False, to tell the user manager application whether or not changing
|
|
|
passwords within Hue is possible.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Authorization
|
|
|
--------------
|
|
|
+### Authorization
|
|
|
|
|
|
Applications may define permission sets for different actions. Administrators
|
|
|
can assign permissions to user groups in the UserAdmin application. To define
|
|
|
@@ -649,8 +618,8 @@ Then you can use this decorator on your view functions to enforce permission:
|
|
|
def delete_financial_report(request):
|
|
|
...
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Using and Installing Thrift
|
|
|
----------------------------
|
|
|
+### Using and Installing Thrift
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
Right now, we check in the generated thrift code.
|
|
|
To generate the code, you'll need the thrift binary version 0.9.0.
|
|
|
Please download from http://thrift.apache.org/.
|
|
|
@@ -658,8 +627,8 @@ Please download from http://thrift.apache.org/.
|
|
|
The modules using ``Thrift`` have some helper scripts like ``regenerate_thrift.sh``
|
|
|
for regenerating the code from the interfaces.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Profiling Hue Apps
|
|
|
-------------------
|
|
|
+### Profiling Hue Apps
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
Hue has a profiling system built in, which can be used to analyze server-side
|
|
|
performance of applications. To enable profiling::
|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -694,14 +663,35 @@ other stats available, take a look at this website:
|
|
|
http://docs.python.org/library/profile.html#pstats.Stats
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-<!--
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
## Django Models
|
|
|
|
|
|
-## Caution: upgrade path
|
|
|
--->
|
|
|
+Each app used to have its own model to store its data (e.g. a SQL query, a workflow). In Hue 3
|
|
|
+a unification of all the models happened and any app now uses a single Document2 model:
|
|
|
+``desktop/core/src/desktop/models.py``. This enables to avoid simply re-use document
|
|
|
+creation, sharing, saving etc...
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+## REST
|
|
|
+Hue is Ajax based and has a REST API used by the browser to communicate (e.g. submit a query or workflow,
|
|
|
+list some S3 files, export a document...). Currently this API is private and subject to change but
|
|
|
+can be easily reused. You would need to GET ``/accounts/login`` to get the CSRF token
|
|
|
+and POST it back along ``username`` and ``password`` and reuse the ``sessionid`` cookie in next
|
|
|
+communication calls.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+<div class="note">
|
|
|
+ http://issues.cloudera.org/browse/HUE-1450 is tracking a more official public API.
|
|
|
+</div>
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Front-end Development
|
|
|
-=====================
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+## Upgrade path
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+After upgrading the version of Hue, running these two commands will make sure the
|
|
|
+database has the correct tables and fields.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ ./build/env/bin/hue syncdb
|
|
|
+ ./build/env/bin/hue migrate
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+## Front-end Development
|
|
|
|
|
|
Developing applications for Hue requires a minimal amount of CSS
|
|
|
(and potentially JavaScript) to use existing functionality. As covered above,
|
|
|
@@ -714,8 +704,7 @@ In a nutshell, front-end development in Hue is using
|
|
|
interactions.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-CSS Styles
|
|
|
-----------
|
|
|
+### CSS Styles
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hue uses [Bootstrap](http://twitter.github.com/bootstrap/) version 2.0 CSS
|
|
|
styles and layouts. They are highly reusable and flexible. Your app doesn't
|
|
|
@@ -725,8 +714,7 @@ app look at home in Hue.
|
|
|
On top of the standard Bootstrap styles, Hue defines a small set of custom
|
|
|
styles in *desktop/core/static/css/jhue.css*.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Defining Styles for Your Application
|
|
|
-------------------------------------
|
|
|
+### Defining Styles for Your Application
|
|
|
|
|
|
When you create your application it will provision a CSS file for you in the
|
|
|
*static/css* directory. For organization purposes, your styles should go here
|
|
|
@@ -751,8 +739,7 @@ prevent you from accidentally colliding with the framework style. Examples:
|
|
|
background: url(../art/paragraph.gif);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Icons
|
|
|
------
|
|
|
+### Icons
|
|
|
|
|
|
You should create an icon for your application that is a transparent png sized
|
|
|
24px by 24px. Your `settings.py` file should point to your icon via the `ICON`
|
|
|
@@ -770,29 +757,26 @@ like this (in your mako template):
|
|
|
<!-- show a trash icon in a link -->
|
|
|
<a href="#something"><i class="icon-trash"></i> Trash</a>
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Static files
|
|
|
-------------
|
|
|
+### Static files
|
|
|
|
|
|
For better performances, Hue uses the Django staticfiles app. If in production mode, if you edit
|
|
|
some static files, you would need to run this command or `make apps`. No actions are needed in
|
|
|
development mode.
|
|
|
-<pre>
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
./build/env/bin/hue collectstatic
|
|
|
-</pre>
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Adding Interactive Elements to Your UI
|
|
|
---------------------------------------
|
|
|
+### Adding Interactive Elements to Your UI
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hue by default loads these JavaScript components:
|
|
|
|
|
|
+* Ko js
|
|
|
* jQuery
|
|
|
-* jQuery.dataTables
|
|
|
* Bootstrap
|
|
|
|
|
|
These are used by some Hue applications, but not loaded by default:
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Knockout js (`desktop/core/static/ext/js/knockout-min.js`)
|
|
|
-* DataTables pagination using the Bootstrap style (`desktop/core/static/ext/js/datatables-paging-0.1.js`)
|
|
|
* jQuery UI (`desktop/core/static/ext/js/jquery/plugins/jquery-ui-autocomplete-1.8.18.min.js`)
|
|
|
|
|
|
These standard components have their own online documentation, which we will
|
|
|
@@ -800,24 +784,44 @@ not repeat here. They let you write interactive behaviors with little or no
|
|
|
JavaScript.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Including Other JavaScript Frameworks
|
|
|
--------------------------------------
|
|
|
+## Debugging Tips and Tricks
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+* Set `DESKTOP_DEBUG=1` as an environment variable if you want logs to go to stderr
|
|
|
+ as well as to the respective log files.
|
|
|
+* Use runserver. If you want to set a CLI breakpoint, just insert
|
|
|
+ `__import__("ipdb").set_trace()`
|
|
|
+ into your code.
|
|
|
+* Django tends to restart its server whenever it notices a file changes. For
|
|
|
+ certain things (like configuration changes), this is not sufficient. Restart
|
|
|
+ the server whole-heartedly.
|
|
|
+* If you find yourself writing a lot of JavaScript, you'll want to disable the
|
|
|
+ JavaScript caching that the server does. At startup Hue reads all your
|
|
|
+ dependencies and JS files into memory to make things faster. You can disable
|
|
|
+ this by executing the runserver command with an environment variable
|
|
|
+ set. Hue will be a little slower, but your JS will always represent what's on
|
|
|
+ the disk. Here's what that looks like:
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ `$ DESKTOP_DEPENDER_DEBUG=1 build/env/bin/hue runserver`
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+* We recommend developing with the Chrome console.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-It is possible to include other JavaScript frameworks to do your development.
|
|
|
-Simply include them to your application's pages. MooTools, Dojo, YUI, etc are
|
|
|
-all fine. Including them represents an additional burden for your users to
|
|
|
-download, and they also make it harder for us to support you, but it is your
|
|
|
-call.
|
|
|
+## Building
|
|
|
+### Documentation
|
|
|
|
|
|
-<!-- ## Adding dynamic data to the nav bar -->
|
|
|
+Building with
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+make docs
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
|
|
|
-<!-- ## Knockout, jQuery -->
|
|
|
+### CSS / LESS
|
|
|
|
|
|
-<!-- ## Lost: Keyboard shortcuts -->
|
|
|
+After changing the CSS in a .less file, rebuilding with:
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+make css
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
|
|
|
+### Internationalization
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Internationalization
|
|
|
-====================
|
|
|
How to update all the messages and compile them::
|
|
|
|
|
|
make locales
|
|
|
@@ -832,47 +836,25 @@ How to create a new locale for an app::
|
|
|
cd $APP_ROOT/src/$APP_NAME/locale
|
|
|
$HUE_ROOT/build/env/bin/pybabel init -D django -i en_US.pot -d . -l fr
|
|
|
|
|
|
+# Testing
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Debugging Tips and Tricks
|
|
|
-=========================
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-* Set `DESKTOP_DEBUG=1` as an environment variable if you want logs to go to stderr
|
|
|
- as well as to the respective log files.
|
|
|
-* Use runserver. If you want to set a CLI breakpoint, just insert
|
|
|
- `__import__("ipdb").set_trace()`
|
|
|
- into your code.
|
|
|
-* Django tends to restart its server whenever it notices a file changes. For
|
|
|
- certain things (like configuration changes), this is not sufficient. Restart
|
|
|
- the server whole-heartedly.
|
|
|
-* If you find yourself writing a lot of JavaScript, you'll want to disable the
|
|
|
- JavaScript caching that the server does. At startup Hue reads all your
|
|
|
- dependencies and JS files into memory to make things faster. You can disable
|
|
|
- this by executing the runserver command with an environment variable
|
|
|
- set. Hue will be a little slower, but your JS will always represent what's on
|
|
|
- the disk. Here's what that looks like:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- `$ DESKTOP_DEPENDER_DEBUG=1 build/env/bin/hue runserver`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-* We recommend developing with the Chrome console.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-The short story
|
|
|
-===============
|
|
|
+## The short story
|
|
|
|
|
|
Install the mini cluster (only once):
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
-$ ./tools/jenkins/jenkins.sh slow
|
|
|
+./tools/jenkins/jenkins.sh slow
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
Run all the tests:
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
-$ build/env/bin/hue test all
|
|
|
+build/env/bin/hue test all
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
Or just some parts of the tests, e.g.:
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
-$ build/env/bin/hue test specific impala
|
|
|
-$ build/env/bin/hue test specific impala.tests:TestMockedImpala
|
|
|
-$ build/env/bin/hue test specific impala.tests:TestMockedImpala.test_basic_flow
|
|
|
+build/env/bin/hue test specific impala
|
|
|
+build/env/bin/hue test specific impala.tests:TestMockedImpala
|
|
|
+build/env/bin/hue test specific impala.tests:TestMockedImpala.test_basic_flow
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jasmine tests (from your browser):
|
|
|
@@ -880,8 +862,7 @@ Jasmine tests (from your browser):
|
|
|
http://localhost:8000/jasmine
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Longer story
|
|
|
-============
|
|
|
+## Longer story
|
|
|
|
|
|
The ``test`` management command prepares the arguments (test app names)
|
|
|
and passes them to nose (django_nose.nose_runner). Nose will then magically
|
|
|
@@ -894,8 +875,7 @@ the word "test" at a word boundary, and nose will find it.
|
|
|
See apps/hello/src/hello/hello_test.py for an example.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Helpful command-line tricks
|
|
|
-===========================
|
|
|
+### Helpful command-line tricks
|
|
|
|
|
|
To run tests that do not depend on Hadoop, use:
|
|
|
build/env/bin/hue test fast
|
|
|
@@ -920,15 +900,13 @@ Point to an Impalad and trigger the Impala tests:
|
|
|
build/env/bin/hue test impala impalad-01.gethue.com
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Run the Jasmine tests
|
|
|
-=====================
|
|
|
+### Run the Jasmine tests
|
|
|
|
|
|
* NodeJS (https://nodejs.org/)
|
|
|
* PhantomJS (npm install -g phantomjs-prebuilt)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Special environment variables
|
|
|
-=============================
|
|
|
+### Special environment variables
|
|
|
|
|
|
DESKTOP_LOGLEVEL=<level>
|
|
|
level can be DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, or CRITICAL
|
|
|
@@ -956,8 +934,7 @@ TEST_IMPALAD_HOST=impalad-01.gethue.com
|
|
|
Point to an Impalad and trigger the Impala tests.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Writing tests that depend on Hadoop
|
|
|
-===================================
|
|
|
+### Writing tests that depend on Hadoop
|
|
|
|
|
|
Use pseudo_hdfs4.py! You should tag such tests with "requires_hadoop", as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -968,21 +945,13 @@ Use pseudo_hdfs4.py! You should tag such tests with "requires_hadoop", as follo
|
|
|
...
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Hudson Configuration
|
|
|
-====================
|
|
|
+### Jenkins Configuration
|
|
|
|
|
|
Because building Hadoop (for the tests that require it) is slow, we've
|
|
|
separated the Hudson builds into "fast" and "slow". Both are run
|
|
|
-via scripts/hudson.sh, which should be kept updated with the latest
|
|
|
+via scripts/jenkins.sh, which should be kept updated with the latest
|
|
|
and greatest in build technologies.
|
|
|
|
|
|
-Headless Windmill
|
|
|
-=================
|
|
|
-Ideally, all you need to do is install xvfb and run "xvfb-run bin/hue test_windmill".
|
|
|
-To debug, however, you'll need to be able to check out what's going on. You can run
|
|
|
-"xvfb-run bash", followed by "x11vnc", and then connect to your X via VNC from another
|
|
|
-machine. This lets you eavesdrop nicely.
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
</div>
|
|
|
</div>
|