---
title: How to configure Hue for your Hadoop cluster
author: admin
type: post
date: 2014-10-02T22:01:37+00:00
url: /how-to-configure-hue-in-your-hadoop-cluster/
sf_thumbnail_type:
- none
sf_thumbnail_link_type:
- link_to_post
sf_detail_type:
- none
sf_page_title:
- 1
sf_page_title_style:
- standard
sf_no_breadcrumbs:
- 1
sf_page_title_bg:
- none
sf_page_title_text_style:
- light
sf_background_image_size:
- cover
sf_social_sharing:
- 1
sf_sidebar_config:
- left-sidebar
sf_left_sidebar:
- Sidebar-2
sf_right_sidebar:
- Sidebar-1
sf_caption_position:
- caption-right
sf_remove_promo_bar:
- 1
slide_template:
- default
categories:
- Administration
- Development
---
Hue is a lightweight Web server that lets you [use Hadoop][1] directly from your browser. Hue is just a ‘view on top of any Hadoop distribution’ and can be installed on any machine.
There are multiples ways (cf. ‘Download’ section of [gethue.com][2]) to install Hue. The next step is then to configure Hue to point to your [Hadoop cluster][3]. By default Hue assumes a local cluster (i.e. there is only one machine) is present. In order to interact with a real cluster, Hue needs to know on which hosts are distributed the Hadoop services.
[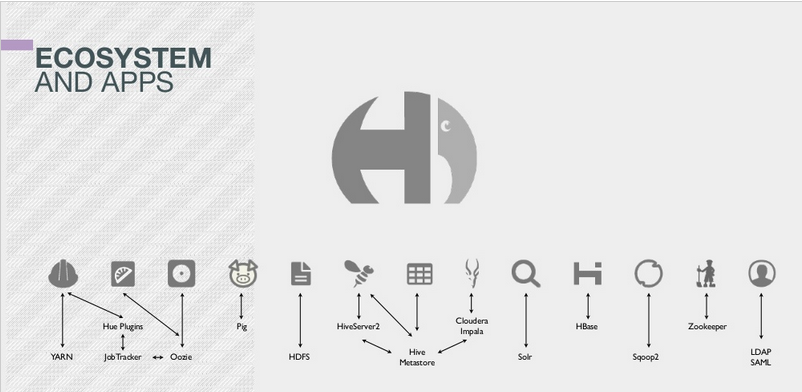 ][4]
## Where is my hue.ini?
Hue main configuration happens in a [hue.ini][5] file. It lists a lot of options but essentially what are the addresses and ports of HDFS, YARN, Oozie, Hive… Depending on the distribution you installed the ini file is located:
* CDH [package][6]: /etc/hue/conf/hue.ini
* A tarball [release][7]: /usr/share/desktop/conf/hue.ini
* [Development][8] version: desktop/conf/pseudo-distributed.ini
* [Cloudera Manager][9]: CM generates all the hue.ini for you, so no hassle 😉 /var/run/cloudera-scm-agent/process/\`ls -alrt /var/run/cloudera-scm-agent/process | grep HUE | tail -1 | awk '{print $9}'\`/hue.ini
**
Note:** To override a value in Cloudera Manager, you need to enter verbatim each mini section from below into the Hue [Safety Valve][10]: Hue Service → Configuration → Service-Wide → Advanced → Hue Service Advanced Configuration Snippet (Safety Valve) for hue_safety_valve.ini
At any time, you can see the path to the hue.ini and what are its values on the [/desktop/dump_config][11] page. Then, for each Hadoop Service, Hue contains a section that needs to be updated with the correct hostnames and ports. Here is an example of the Hive section in the ini file:
{{< highlight bash >}}[beeswax]
# Host where HiveServer2 is running.
hive_server_host=localhost
{{< /highlight >}}
To point to another server, just replaced the host value by 'hiveserver.ent.com':
{{< highlight bash >}}[beeswax]
# Host where HiveServer2 is running.
hive_server_host=hiveserver.ent.com
{{< /highlight >}}
**Note: **Any line starting with a # is considered as a comment so is not used.
**Note: **The list of mis-configured services are listed on the [/about/admin_wizard][12] page.
**Note: **After each change in the ini file, Hue should be restarted to pick it up.
**Note:** In some cases, as explained in [how to configure Hadoop for Hue documentation][13], the API of these services needs to be turned on and Hue set as proxy user.
## Removing Apps
[This article][14] shows how to configure Hue to not show certain apps. The list of all the apps is available on the /desktop/dump_config page of Hue.
Here are the main sections that you will need to update in order to have each service accessible in Hue:
## HDFS
This is required for [listing or creating files][15]. Replace localhost by the real address of the NameNode (usually http://localhost:50070).
Enter this in hdfs-site.xml to enable WebHDFS in the NameNode and DataNodes:
{{< highlight xml >}}
dfs.webhdfs.enabled
true
{{< /highlight >}}
Configure Hue as a proxy user for all other users and groups, meaning it may submit a request on behalf of any other user. Add to core-site.xml:
{{< highlight xml >}}
hadoop.proxyuser.hue.hosts
*
hadoop.proxyuser.hue.groups
*
{{< /highlight >}}
Then, if the Namenode is on another host than Hue, don't forget to update in the hue.ini:
{{< highlight bash >}}[hadoop]
[[hdfs_clusters]]
[[[default]]]
# Enter the filesystem uri
fs_defaultfs=hdfs://localhost:8020
# Use WebHdfs/HttpFs as the communication mechanism.
# Domain should be the NameNode or HttpFs host.
webhdfs_url=http://localhost:50070/webhdfs/v1
{{< /highlight >}}
## YARN
The Resource Manager is often on http://localhost:8088 by default. The ProxyServer and Job History servers also needs to be specified. Then Job Browser will let you [list and kill running applications][16] and get their logs.
{{< highlight bash >}}[hadoop]
[[yarn_clusters]]
[[[default]]]
# Enter the host on which you are running the ResourceManager
resourcemanager_host=localhost
# Whether to submit jobs to this cluster
submit_to=True
# URL of the ResourceManager API
resourcemanager_api_url=http://localhost:8088
# URL of the ProxyServer API
proxy_api_url=http://localhost:8088
# URL of the HistoryServer API
history_server_api_url=http://localhost:19888
{{< /highlight >}}
## Hive
Here we need a running HiveServer2 in order to [send SQL queries][17].
{{< highlight bash >}}[beeswax]
# Host where HiveServer2 is running.
hive_server_host=localhost
{{< /highlight >}}
Note:
If HiveServer2 is on another machine and you are using security or customized HiveServer2 configuration, you will need to copy the hive-site.xml on the Hue machine too:
{{< highlight bash >}}[beeswax]
# Host where HiveServer2 is running.
hive_server_host=localhost
\# Hive configuration directory, where hive-site.xml is located
hive_conf_dir=/etc/hive/conf
{{< /highlight >}}
## Impala
We need to specify one of the Impalad address for [interactive SQL][17] in the Impala app.
{{< highlight bash >}}[impala]
# Host of the Impala Server (one of the Impalad)
server_host=localhost
{{< /highlight >}}
## Solr Search
We just need to specify the address of a Solr Cloud (or non Cloud Solr), then [interactive dashboards][18] capabilities are unleashed!
{{< highlight bash >}}[search]
# URL of the Solr Server
solr_url=http://localhost:8983/solr/
{{< /highlight >}}
## Oozie
An Oozie server should be up and running before [submitting or monitoring workflows][19].
{{< highlight bash >}}[liboozie]
# The URL where the Oozie service runs on.
oozie_url=http://localhost:11000/oozie
{{< /highlight >}}
## Pig
The [Pig Editor][20] requires Oozie to be setup with its [sharelib][21].
## HBase
The HBase app works with a HBase Thrift Server version 1. It lets you [browse, query and edit HBase tables][22].
{{< highlight bash >}}[hbase]
# Comma-separated list of HBase Thrift server 1 for clusters in the format of '(name|host:port)'.
hbase_clusters=(Cluster|localhost:9090)
{{< /highlight >}}
## Sentry
Hue just needs to point to the machine with the Sentry server running.
{{< highlight bash >}}[libsentry]
# Hostname or IP of server.
hostname=localhost
{{< /highlight >}}
And that’s it! Now Hue will let you do Big Data directly from your browser without touching the command line! You can then follow-up with some [tutorials][23].
As usual feel free to comment and send feedback on the [hue-user][24] list or [@gethue][25]!
[1]: http://vimeo.com/88256132
[2]: http://gethue.com
[3]: https://gethue.com/yahoo-hadoop-meetup-integrate-hue-with-your-hadoop-cluster/
[4]: https://cdn.gethue.com/uploads/2014/10/hue-ecosystem.png
[5]: https://github.com/cloudera/hue/blob/master/desktop/conf.dist/hue.ini
[6]: http://archive.cloudera.com/cdh5/one-click-install/
[7]: https://gethue.com/category/release/
[8]: https://gethue.com/how-to-build-hue-on-ubuntu-14-04-trusty/
[9]: https://gethue.com/hadoop-tutorial-how-to-create-a-real-hadoop-cluster-in-10-minutes/
[10]: http://www.cloudera.com/content/cloudera/en/documentation/cloudera-manager/v5-1-x/Cloudera-Manager-Managing-Clusters/cm5mc_config_snippet.html
[11]: http://127.0.0.1:8888/desktop/dump_config
[12]: http://127.0.0.1:8888/about/admin_wizard
[13]: http://www.cloudera.com/content/cloudera/en/documentation/cdh5/latest/CDH5-Installation-Guide/cdh5ig_cdh_hue_configure.html
[14]: https://gethue.com/solr-search-ui-only/
[15]: https://gethue.com/demo-hdfs-file-operations-made-easy-with-hue/
[16]: https://gethue.com/using-hadoop-mr2-and-yarn-with-an-alternative-job/
[17]: https://gethue.com/hadoop-tutorial-new-impala-and-hive-editors/
[18]: https://gethue.com/hadoop-search-dynamic-search-dashboards-with-solr/
[19]: https://gethue.com/category/oozie/
[20]: https://gethue.com/hadoop-tutorial-language-assistant-in-pig-editor-with/
[21]: http://blog.cloudera.com/blog/2014/05/how-to-use-the-sharelib-in-apache-oozie-cdh-5/
[22]: https://gethue.com/hue-2-5-and-its-hbase-app-is-out/
[23]: https://gethue.com/category/tutorial/
[24]: http://groups.google.com/a/cloudera.org/group/hue-user
[25]: https://twitter.com/gethue
][4]
## Where is my hue.ini?
Hue main configuration happens in a [hue.ini][5] file. It lists a lot of options but essentially what are the addresses and ports of HDFS, YARN, Oozie, Hive… Depending on the distribution you installed the ini file is located:
* CDH [package][6]: /etc/hue/conf/hue.ini
* A tarball [release][7]: /usr/share/desktop/conf/hue.ini
* [Development][8] version: desktop/conf/pseudo-distributed.ini
* [Cloudera Manager][9]: CM generates all the hue.ini for you, so no hassle 😉 /var/run/cloudera-scm-agent/process/\`ls -alrt /var/run/cloudera-scm-agent/process | grep HUE | tail -1 | awk '{print $9}'\`/hue.ini
**
Note:** To override a value in Cloudera Manager, you need to enter verbatim each mini section from below into the Hue [Safety Valve][10]: Hue Service → Configuration → Service-Wide → Advanced → Hue Service Advanced Configuration Snippet (Safety Valve) for hue_safety_valve.ini
At any time, you can see the path to the hue.ini and what are its values on the [/desktop/dump_config][11] page. Then, for each Hadoop Service, Hue contains a section that needs to be updated with the correct hostnames and ports. Here is an example of the Hive section in the ini file:
{{< highlight bash >}}[beeswax]
# Host where HiveServer2 is running.
hive_server_host=localhost
{{< /highlight >}}
To point to another server, just replaced the host value by 'hiveserver.ent.com':
{{< highlight bash >}}[beeswax]
# Host where HiveServer2 is running.
hive_server_host=hiveserver.ent.com
{{< /highlight >}}
**Note: **Any line starting with a # is considered as a comment so is not used.
**Note: **The list of mis-configured services are listed on the [/about/admin_wizard][12] page.
**Note: **After each change in the ini file, Hue should be restarted to pick it up.
**Note:** In some cases, as explained in [how to configure Hadoop for Hue documentation][13], the API of these services needs to be turned on and Hue set as proxy user.
## Removing Apps
[This article][14] shows how to configure Hue to not show certain apps. The list of all the apps is available on the /desktop/dump_config page of Hue.
Here are the main sections that you will need to update in order to have each service accessible in Hue:
## HDFS
This is required for [listing or creating files][15]. Replace localhost by the real address of the NameNode (usually http://localhost:50070).
Enter this in hdfs-site.xml to enable WebHDFS in the NameNode and DataNodes:
{{< highlight xml >}}
dfs.webhdfs.enabled
true
{{< /highlight >}}
Configure Hue as a proxy user for all other users and groups, meaning it may submit a request on behalf of any other user. Add to core-site.xml:
{{< highlight xml >}}
hadoop.proxyuser.hue.hosts
*
hadoop.proxyuser.hue.groups
*
{{< /highlight >}}
Then, if the Namenode is on another host than Hue, don't forget to update in the hue.ini:
{{< highlight bash >}}[hadoop]
[[hdfs_clusters]]
[[[default]]]
# Enter the filesystem uri
fs_defaultfs=hdfs://localhost:8020
# Use WebHdfs/HttpFs as the communication mechanism.
# Domain should be the NameNode or HttpFs host.
webhdfs_url=http://localhost:50070/webhdfs/v1
{{< /highlight >}}
## YARN
The Resource Manager is often on http://localhost:8088 by default. The ProxyServer and Job History servers also needs to be specified. Then Job Browser will let you [list and kill running applications][16] and get their logs.
{{< highlight bash >}}[hadoop]
[[yarn_clusters]]
[[[default]]]
# Enter the host on which you are running the ResourceManager
resourcemanager_host=localhost
# Whether to submit jobs to this cluster
submit_to=True
# URL of the ResourceManager API
resourcemanager_api_url=http://localhost:8088
# URL of the ProxyServer API
proxy_api_url=http://localhost:8088
# URL of the HistoryServer API
history_server_api_url=http://localhost:19888
{{< /highlight >}}
## Hive
Here we need a running HiveServer2 in order to [send SQL queries][17].
{{< highlight bash >}}[beeswax]
# Host where HiveServer2 is running.
hive_server_host=localhost
{{< /highlight >}}
Note:
If HiveServer2 is on another machine and you are using security or customized HiveServer2 configuration, you will need to copy the hive-site.xml on the Hue machine too:
{{< highlight bash >}}[beeswax]
# Host where HiveServer2 is running.
hive_server_host=localhost
\# Hive configuration directory, where hive-site.xml is located
hive_conf_dir=/etc/hive/conf
{{< /highlight >}}
## Impala
We need to specify one of the Impalad address for [interactive SQL][17] in the Impala app.
{{< highlight bash >}}[impala]
# Host of the Impala Server (one of the Impalad)
server_host=localhost
{{< /highlight >}}
## Solr Search
We just need to specify the address of a Solr Cloud (or non Cloud Solr), then [interactive dashboards][18] capabilities are unleashed!
{{< highlight bash >}}[search]
# URL of the Solr Server
solr_url=http://localhost:8983/solr/
{{< /highlight >}}
## Oozie
An Oozie server should be up and running before [submitting or monitoring workflows][19].
{{< highlight bash >}}[liboozie]
# The URL where the Oozie service runs on.
oozie_url=http://localhost:11000/oozie
{{< /highlight >}}
## Pig
The [Pig Editor][20] requires Oozie to be setup with its [sharelib][21].
## HBase
The HBase app works with a HBase Thrift Server version 1. It lets you [browse, query and edit HBase tables][22].
{{< highlight bash >}}[hbase]
# Comma-separated list of HBase Thrift server 1 for clusters in the format of '(name|host:port)'.
hbase_clusters=(Cluster|localhost:9090)
{{< /highlight >}}
## Sentry
Hue just needs to point to the machine with the Sentry server running.
{{< highlight bash >}}[libsentry]
# Hostname or IP of server.
hostname=localhost
{{< /highlight >}}
And that’s it! Now Hue will let you do Big Data directly from your browser without touching the command line! You can then follow-up with some [tutorials][23].
As usual feel free to comment and send feedback on the [hue-user][24] list or [@gethue][25]!
[1]: http://vimeo.com/88256132
[2]: http://gethue.com
[3]: https://gethue.com/yahoo-hadoop-meetup-integrate-hue-with-your-hadoop-cluster/
[4]: https://cdn.gethue.com/uploads/2014/10/hue-ecosystem.png
[5]: https://github.com/cloudera/hue/blob/master/desktop/conf.dist/hue.ini
[6]: http://archive.cloudera.com/cdh5/one-click-install/
[7]: https://gethue.com/category/release/
[8]: https://gethue.com/how-to-build-hue-on-ubuntu-14-04-trusty/
[9]: https://gethue.com/hadoop-tutorial-how-to-create-a-real-hadoop-cluster-in-10-minutes/
[10]: http://www.cloudera.com/content/cloudera/en/documentation/cloudera-manager/v5-1-x/Cloudera-Manager-Managing-Clusters/cm5mc_config_snippet.html
[11]: http://127.0.0.1:8888/desktop/dump_config
[12]: http://127.0.0.1:8888/about/admin_wizard
[13]: http://www.cloudera.com/content/cloudera/en/documentation/cdh5/latest/CDH5-Installation-Guide/cdh5ig_cdh_hue_configure.html
[14]: https://gethue.com/solr-search-ui-only/
[15]: https://gethue.com/demo-hdfs-file-operations-made-easy-with-hue/
[16]: https://gethue.com/using-hadoop-mr2-and-yarn-with-an-alternative-job/
[17]: https://gethue.com/hadoop-tutorial-new-impala-and-hive-editors/
[18]: https://gethue.com/hadoop-search-dynamic-search-dashboards-with-solr/
[19]: https://gethue.com/category/oozie/
[20]: https://gethue.com/hadoop-tutorial-language-assistant-in-pig-editor-with/
[21]: http://blog.cloudera.com/blog/2014/05/how-to-use-the-sharelib-in-apache-oozie-cdh-5/
[22]: https://gethue.com/hue-2-5-and-its-hbase-app-is-out/
[23]: https://gethue.com/category/tutorial/
[24]: http://groups.google.com/a/cloudera.org/group/hue-user
[25]: https://twitter.com/gethue
 ][4]
## Where is my hue.ini?
Hue main configuration happens in a [hue.ini][5] file. It lists a lot of options but essentially what are the addresses and ports of HDFS, YARN, Oozie, Hive… Depending on the distribution you installed the ini file is located:
* CDH [package][6]: /etc/hue/conf/hue.ini
* A tarball [release][7]: /usr/share/desktop/conf/hue.ini
* [Development][8] version: desktop/conf/pseudo-distributed.ini
* [Cloudera Manager][9]: CM generates all the hue.ini for you, so no hassle 😉 /var/run/cloudera-scm-agent/process/\`ls -alrt /var/run/cloudera-scm-agent/process | grep HUE | tail -1 | awk '{print $9}'\`/hue.ini
**
Note:** To override a value in Cloudera Manager, you need to enter verbatim each mini section from below into the Hue [Safety Valve][10]: Hue Service → Configuration → Service-Wide → Advanced → Hue Service Advanced Configuration Snippet (Safety Valve) for hue_safety_valve.ini
At any time, you can see the path to the hue.ini and what are its values on the [/desktop/dump_config][11] page. Then, for each Hadoop Service, Hue contains a section that needs to be updated with the correct hostnames and ports. Here is an example of the Hive section in the ini file:
{{< highlight bash >}}[beeswax]
# Host where HiveServer2 is running.
hive_server_host=localhost
{{< /highlight >}}
To point to another server, just replaced the host value by 'hiveserver.ent.com':
{{< highlight bash >}}[beeswax]
# Host where HiveServer2 is running.
hive_server_host=hiveserver.ent.com
{{< /highlight >}}
**Note: **Any line starting with a # is considered as a comment so is not used.
**Note: **The list of mis-configured services are listed on the [/about/admin_wizard][12] page.
**Note: **After each change in the ini file, Hue should be restarted to pick it up.
**Note:** In some cases, as explained in [how to configure Hadoop for Hue documentation][13], the API of these services needs to be turned on and Hue set as proxy user.
## Removing Apps
[This article][14] shows how to configure Hue to not show certain apps. The list of all the apps is available on the /desktop/dump_config page of Hue.
Here are the main sections that you will need to update in order to have each service accessible in Hue:
## HDFS
This is required for [listing or creating files][15]. Replace localhost by the real address of the NameNode (usually http://localhost:50070).
Enter this in hdfs-site.xml to enable WebHDFS in the NameNode and DataNodes:
{{< highlight xml >}}
][4]
## Where is my hue.ini?
Hue main configuration happens in a [hue.ini][5] file. It lists a lot of options but essentially what are the addresses and ports of HDFS, YARN, Oozie, Hive… Depending on the distribution you installed the ini file is located:
* CDH [package][6]: /etc/hue/conf/hue.ini
* A tarball [release][7]: /usr/share/desktop/conf/hue.ini
* [Development][8] version: desktop/conf/pseudo-distributed.ini
* [Cloudera Manager][9]: CM generates all the hue.ini for you, so no hassle 😉 /var/run/cloudera-scm-agent/process/\`ls -alrt /var/run/cloudera-scm-agent/process | grep HUE | tail -1 | awk '{print $9}'\`/hue.ini
**
Note:** To override a value in Cloudera Manager, you need to enter verbatim each mini section from below into the Hue [Safety Valve][10]: Hue Service → Configuration → Service-Wide → Advanced → Hue Service Advanced Configuration Snippet (Safety Valve) for hue_safety_valve.ini
At any time, you can see the path to the hue.ini and what are its values on the [/desktop/dump_config][11] page. Then, for each Hadoop Service, Hue contains a section that needs to be updated with the correct hostnames and ports. Here is an example of the Hive section in the ini file:
{{< highlight bash >}}[beeswax]
# Host where HiveServer2 is running.
hive_server_host=localhost
{{< /highlight >}}
To point to another server, just replaced the host value by 'hiveserver.ent.com':
{{< highlight bash >}}[beeswax]
# Host where HiveServer2 is running.
hive_server_host=hiveserver.ent.com
{{< /highlight >}}
**Note: **Any line starting with a # is considered as a comment so is not used.
**Note: **The list of mis-configured services are listed on the [/about/admin_wizard][12] page.
**Note: **After each change in the ini file, Hue should be restarted to pick it up.
**Note:** In some cases, as explained in [how to configure Hadoop for Hue documentation][13], the API of these services needs to be turned on and Hue set as proxy user.
## Removing Apps
[This article][14] shows how to configure Hue to not show certain apps. The list of all the apps is available on the /desktop/dump_config page of Hue.
Here are the main sections that you will need to update in order to have each service accessible in Hue:
## HDFS
This is required for [listing or creating files][15]. Replace localhost by the real address of the NameNode (usually http://localhost:50070).
Enter this in hdfs-site.xml to enable WebHDFS in the NameNode and DataNodes:
{{< highlight xml >}}