2014-10-07-apache-sentry-made-easy-with-the-new-hue-security-app.md 6.6 KB
title: Apache Sentry made easy with the new Hue Security App author: admin type: post date: 2014-10-07T20:24:42+00:00 url: /apache-sentry-made-easy-with-the-new-hue-security-app/ sf_thumbnail_type:
- none sf_thumbnail_link_type:
- link_to_post sf_detail_type:
- none sf_page_title:
- 1 sf_page_title_style:
- standard sf_no_breadcrumbs:
- 1 sf_page_title_bg:
- none sf_page_title_text_style:
- light sf_background_image_size:
- cover sf_social_sharing:
- 1 sf_sidebar_config:
- left-sidebar sf_left_sidebar:
- Sidebar-2 sf_right_sidebar:
- Sidebar-1 sf_caption_position:
- caption-right sf_remove_promo_bar:
- 1 slide_template:
- default categories:
Hi Hadoop Sheriffs,
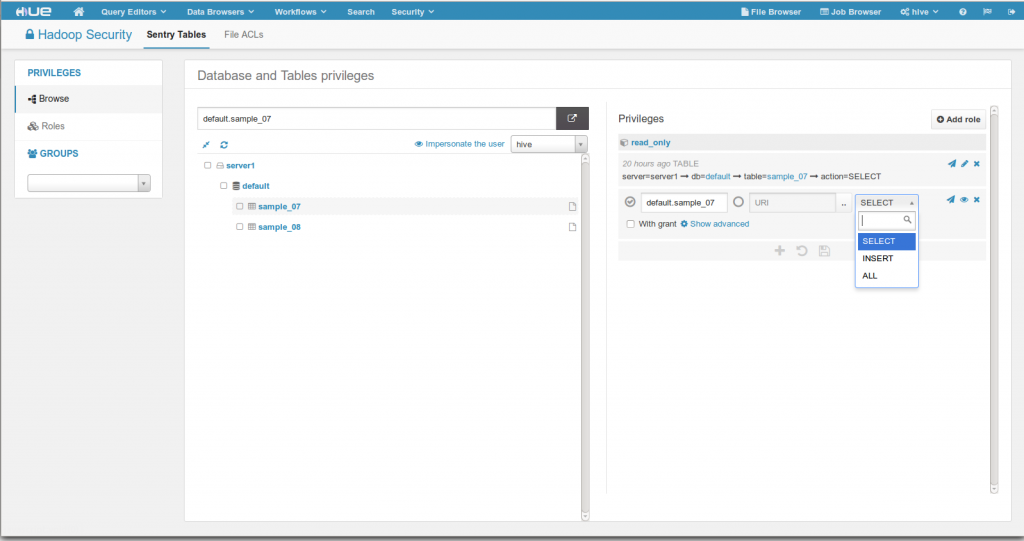
In order to support the growth of the Apache Sentry project and make it easier to secure your cluster, a new app was added into Hue. Sentry privileges determine which Hive / Impala databases and tables a user can see or modify. The Security App let’s you create/edit/delete Roles and Privileges directly from your browser (there is no sentry-provider.ini file to edit anymore).
Here is a video showing how the app works:
Main features:
- Bulk edit roles and privileges
- Visualize/edit roles and privileges on a database tree
- WITH GRANT OPTION support
- Impersonate a user to see which databases and table he can see
To have Hue point to a Sentry service and another host, modify these hue.ini properties:
{{< highlight bash >}}[libsentry]
# Hostname or IP of server.
hostname=localhost
# Port the sentry service is running on.
port=8038
# Sentry configuration directory, where sentry-site.xml is located.
sentry_conf_dir=/etc/sentry/conf
{{< /highlight >}}
Hue will also automatically pick up the server name of HiveServer2 from the sentry-site.xml file of /etc/hive/conf.
And that’s it, you can know specify who can see/do what directly in a Web UI! The app sits on top of the standard Sentry API and so it fully compatible with Sentry. Next planned features will bring Solr Collections, HBase privilege management as well as more bulk operations and a tighter integration with HDFS.
As usual, feel free to continue to send us questions and feedback on the hue-user list or @gethue!
Notes
To be able to edit roles and privileges in Hue, the logged-in Hue user needs to belong to a group in Hue that is also an admin group in Sentry (whatever UserGroupMapping Sentry is using, the corresponding groups must exist in Hue or need to be entered manually). For example, our 'hive' user belongs to a 'hive' group in Hue and also to a 'hive' group in Sentry:
{{< highlight xml >}}
sentry.service.admin.group
hive,impala,hue
{{< /highlight >}}
Notes
- Create a role in the Sentry app through Hue
- Grant privileges to that role such that the role can see the database in the Sentry app
- Create a group in Hue with the same name as the role in Sentry
- Grant that role to a user in Hue
- Ensure that the user in Hue has an equivalent O/S level
- Ensure a user has an O/S level account on all hosts and that user is part of a group with the same name as the group in Hue (this assumes that the default ShellBasedUnixGroupsMapping is set for HDFS in CM)
Notes
We are using CDH5.2+ with Kerberos MIT and Sentry configured. The app also works in non secure mode.
Our users are:
- hive (admin) belongs to the hive group
- user1_1 belongs to the user_group1 group
- user2_1 belongs to the user_group2 group
We synced the Unix users/groups into Hue with these commands:
{{< highlight bash >}}export HUE_CONF_DIR="/var/run/cloudera-scm-agent/process/`ls -alrt /var/run/cloudera-scm-agent/process | grep HUE | tail -1 | awk '{print $9}'`"
build/env/bin/hue useradmin_sync_with_unix -min-uid=1000
{{< /highlight >}}
If using the package version and has the CDH repository register, install sentry with:
{{< highlight bash >}}sudo apt-get install sentry
{{< /highlight >}}
If using Kerberos, make sure ‘hue’ is allowed to connect to Sentry in /etc/sentry/conf/sentry-site.xml:
{{< highlight xml >}}
sentry.service.allow.connect
impala,hive,solr,hue
{{< /highlight >}}
Here is an example of sentry-site.xml
Here is an example of sentry-site.xml
{{< highlight xml >}}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
sentry.service.security.mode
none
sentry.service.admin.group
hive,romain
sentry.service.allow.connect
impala,hive,solr
sentry.store.jdbc.url
jdbc:derby:;databaseName=sentry_store_db;create=true
sentry.store.jdbc.driver
org.apache.derby.jdbc.EmbeddedDriver
sentry.store.jdbc.password
aaa
{{< /highlight >}}
For testing purposes, here is how to create the initial Sentry database:
{{< highlight bash >}}romain@runreal:~/projects/hue$ sentry -command schema-tool -initSchema -conffile /etc/sentry/conf/sentry-site.xml -dbType derby
{{< /highlight >}}
And start the service:
{{< highlight bash >}}sentry -command service -conffile /etc/sentry/conf/sentry-site.xml
{{< /highlight >}}
Note
In Sentry 1.5, you will need to specify a ‘entry.store.jdbc.password’ property in the sentry-site.xml, if not you will get:
{{< highlight bash >}}Caused by: org.apache.sentry.provider.db.service.thrift.SentryConfigurationException: Error reading sentry.store.jdbc.password
{{< /highlight >}}